Installing Drupal
The below example demonstrates the from-scratch setup of a Drupal application for local development. A similar process can easily be used to configure an environment of any other type. This assumes that Warden has been previously started via warden svc up as part of the installation procedure.
Create a new directory on your host machine at the location of your choice and then jump into the new directory to get started:
mkdir -p ~/Sites/exampleproject cd ~/Sites/exampleproject
From the root of your new project directory, run
env-initto create the.envfile with configuration needed for Warden and Docker to work with the project.warden env-init exampleproject drupal
The result of this command is a
.envfile in the project root (tip: commit this to your VCS to share the configuration with other team members) having the following contents:WARDEN_ENV_NAME=exampleproject WARDEN_ENV_TYPE=drupal WARDEN_WEB_ROOT=/ TRAEFIK_DOMAIN=tdpl.test TRAEFIK_SUBDOMAIN=app DB_DISTRIBUTION=mariadb DB_DISTRIBUTION_VERSION=10.4 NODE_VERSION=18 COMPOSER_VERSION=2 PHP_VERSION=8.2 PHP_XDEBUG_3=1 WARDEN_DB=1 WARDEN_RABBITMQ=0 WARDEN_REDIS=0 RABBITMQ_VERSION=3.8 WARDEN_SYNC_IGNORE= WARDEN_ALLURE=0 WARDEN_SELENIUM=0 WARDEN_SELENIUM_DEBUG=0 WARDEN_BLACKFIRE=0 BLACKFIRE_CLIENT_ID= BLACKFIRE_CLIENT_TOKEN= BLACKFIRE_SERVER_ID= BLACKFIRE_SERVER_TOKEN=
Sign an SSL certificate for use with the project (the input here should match the value of
TRAEFIK_DOMAINin the above.envexample file):warden sign-certificate exampleproject.test
Next you’ll want to start the project environment:
warden env up
Warning
If you encounter an error about
Mounts denied, follow the instructions in the error message and runwarden env upagain.Drop into a shell within the project environment. Commands following this step in the setup procedure will be run from within the
php-fpmdocker container this launches you into:warden shell
Initialize project source files using composer create-project and then move them into place:
composer create-project drupal/recommended-project /tmp/exampleproject rsync -a /tmp/exampleproject/ /var/www/html/ rm -rf /tmp/exampleproject/
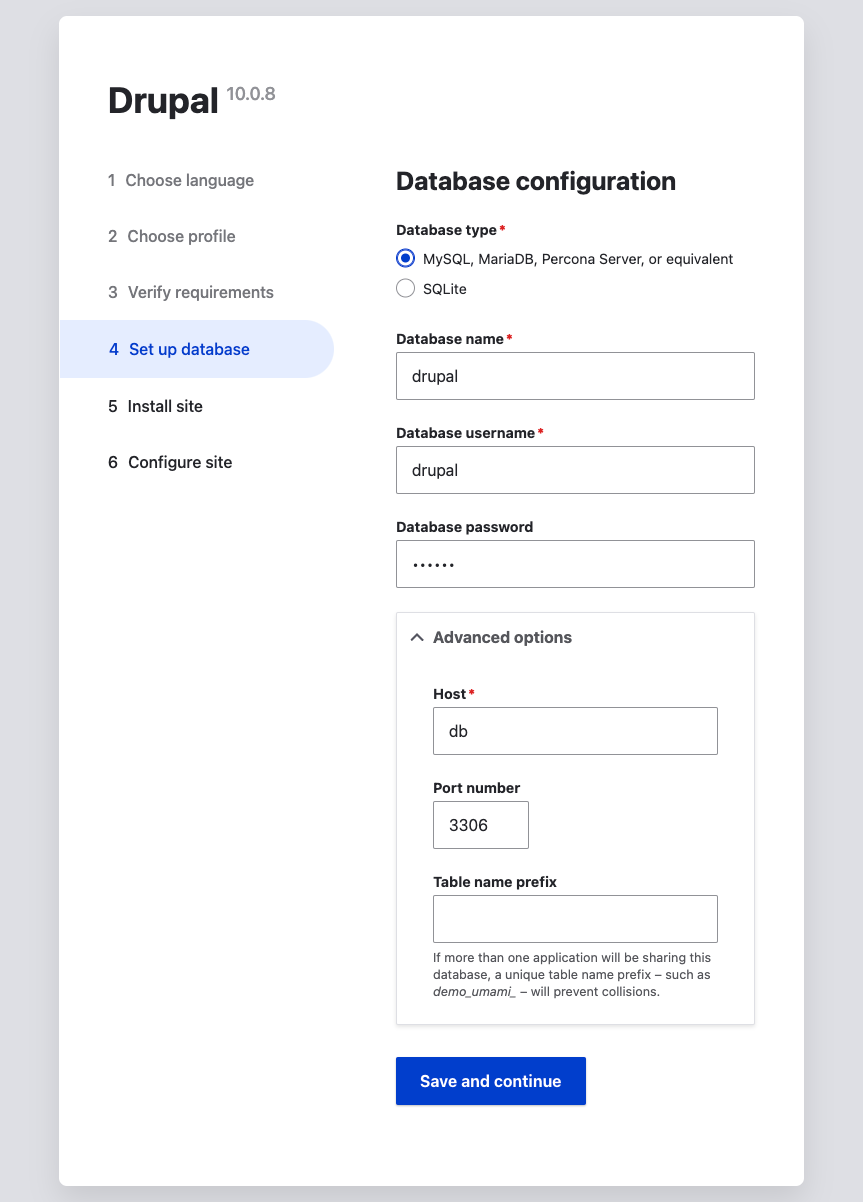
Launch the Installation Wizard in your browser and follow the instructions:
The new application will be at https://app.exampleproject.test/ (or app.what-you-called-your-project.test).
The SQL Credentials that need to be configured are “db” as the host, and “drupal” as the username, password, and database.
Note
To completely destroy the exampleproject environment we just created, run warden env down -v to tear down the project’s Docker containers, volumes, etc.